QuickBooks Job Costing When Using A Payroll Service
Using ‘Zero-Dollar Checks’ to Record Payroll Costs by Job and Class If you use an outside payroll service to process your payroll, using zero-dollar checks may be the easiest way to record payroll expenses by job and/or class (department).
Apr. 17, 2008
From the April/May 2008 Issue
Using ‘Zero-Dollar Checks’ to Record Payroll Costs by Job and
Class If you use an outside payroll service to process your payroll, using zero-dollar
checks may be the easiest way to record payroll expenses by job and/or class
(department). This solution works really well for contractors or other businesses
who need to track and manage labor costs at the job or department level, but
who use an outside service to handle payroll.
Before going into the specifics of the solution, it is important to note that
because the client will not be using any of the payroll features in QuickBooks,
he or she won’t be able to use any of the QuickBooks payroll reports (e.g.,
Payroll Summary, Payroll Liability Balances) or any of the payroll tax reporting
features. Also, this method only approximates (within a few dollars) the payroll
costs for jobs and classes, meaning that the amount of payroll expense allocated
to each job and class will be based on the average hourly payroll costs for
each person in each job. Here are the steps for making this all work.
- To get started, you can completely turn off the payroll option in QuickBooks
Preferences so you’ll never see any warnings about downloading tax tables
or setting up your payroll. - Using a journal entry, enter the totals for your payroll into the general
ledger just as you normally do when using a payroll service. This entry should
credit the bank account for net pay and debit the gross wages, payroll taxes,
and other accounts as necessary (see
Figure 1). After recording the entry in Figure 1, your general ledger
is accurate and up to date, but no job costs have been recorded. The rest
of the steps below provide a self-zeroing entry to record all the job and
class information you need in order to generate job cost reports. - Compute the average cost incurred to place one person on any given job
for one hour. To calculate this amount, you should look at your total payroll
expenses for a given period (e.g., last quarter) including payroll taxes and
workers’ compensation, subtract all payroll expenses that are not job
related (e.g., officer salaries), and then divide by the total number of hours
all employees worked on all jobs during the period. For the purposes of this
section, we will assume the average hourly expense is $18. - Create a Bank account called Payroll Service Clearing. This will be a clearing
account used to record the zero-dollar checks for the payroll job costing. - Create an Expense account called Payroll Job Costs. This is also a clearing
account that will only show balances on job cost reports such as P&L by
Job. Note: If you have long-term contracts whereby you capture job costs on
the balance sheet in an asset account, you should use an Other Current Asset
instead of an expense for Payroll Job Costs. Then, continue with the setup
and transactions shown in this method. - Edit each existing “Service” Item in your Item list, making
them two-sided Items. Enter “Payroll Costs for Jobs and Classes”
in the Description on Purchase Transactions field, enter “18.00”
in the Cost field, and enter “Payroll Job Costs” in the Expense
Account field (see
Figure 2). Then click OK to save your changes. Note: This change to your
Service Items will have no effect on their use in Sales Receipts or Invoices. - Create an Other Name record (not an Employee record) for each employee.
(See
Figure 3.) - Enter daily timesheet information for each employee using the Other Name
record you just created. On each timesheet, include the Service Item, the
name of the job on which the employee worked and the class (if applicable). - To record job costs for each paycheck, open the Write Checks window and
select Payroll Service Clearing from the Account drop-down menu. - Enter the employee’s name (Other Name) on the Pay to the Order of
field of the Check (see
Figure 4). Then press TAB. - QuickBooks will notify you that the name you entered has timesheet data
in the file and ask if you want to use this information when creating this
check (see
Figure 5). Click Yes. - Enter 01/01/2007 in the Start Date field and 01/31/2007 in the End Date
field. Then click OK. Select the period for which you want to job cost payroll
expenses. If you use this method monthly, enter the beginning and ending date
of the month. If you use this method quarterly, enter the beginning and ending
date for the quarter (see
Figure 6). - 13. QuickBooks will then import the timesheet information into the Items
tab of the Check, multiplying the number of hours the employee worked by the
average cost per hour to place the employee on any given job (see
Figure 7). - Click the Expenses tab and then enter Payroll Costs in the Account field
and the amount of the check as a negative number in the Amount field (see
Figure 8). Since you already used a General Journal Entry to update the
General Ledger for payroll expenses, payroll liabilities and bank accounts,
it is very important that this check not increase the balance in the Payroll
Job Costs expense account. If it did, it would overstate expenses for the
period. You must therefore zero-out the amount of the check as shown in Figure
8. - Click Save & Close to record the zero-dollar check. The accounting behind
the scenes: Essentially, this method uses a Check as a zero-dollar journal
entry that feeds the job cost and class reports. The Items tab (Figure 7)
increases (debits) the balance in the Payroll Job Costs expense account by
$2,988, allocating the amount over each job and class on which Mike Mazuki
worked for the period. The Expenses tab (Figure 8) decreases (credits) the
balance in the Payroll Job Costs expense account but does not affect job or
class information. The job cost and class reports will therefore show the
expenses by job and class, but the net effect on the General Ledger (e.g.,
the Profit & Loss Standard report) will be zero. - Review the Profit & Loss by Job report to confirm that payroll expenses
now show for specific jobs (see
Figure 9). Be sure to include the date of the Zero Check created above
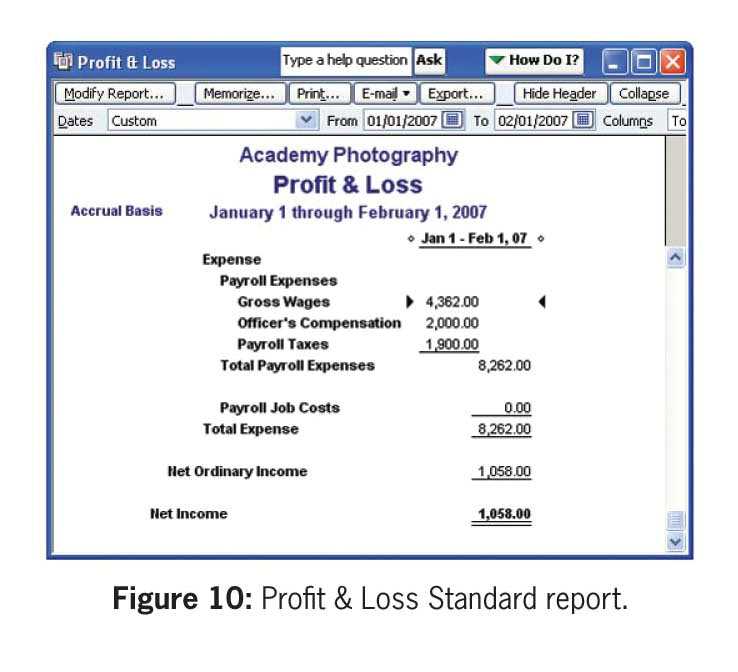
(02/01/2007) in your report. - However, the Profit & Loss Standard report (and the general ledger
as a whole) does not show any balance in the Payroll Job Costs account because
you zeroed this account out when you recorded the check (see
Figure 10).
